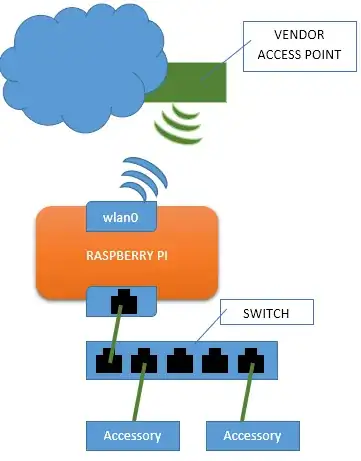
This question is well due for an updated answer. Here's what worked for me, with explanations, so it can be tailored to suit.
This is applicable to a fresh Raspberry Pi OS Lite install, specifically 2023-05-03-raspios-bullseye-arm64-lite, configured for SSH access and connected over Ethernet. YMMV.
- Install
dnsmasq.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install dnsmasq
- Configure
dhcpcd.
Add to the bottom of /etc/dhcpcd.conf:
interface eth0
static ip_address=192.168.2.1/24
nogateway
The nogateway prevents the Pi from prioritising Ethernet as a potential route to the Internet, since it's now strictly a downstream port. Obviously static sets a static IP for the Ethernet port. This will play well with dnsmasq and provides a predictable gateway address for the clients.
The choice is fairly arbitrary, but I picked something distinctive that aligns with the other answers. If your WiFi happens to be on that subnet, you might want to pick something else to make it easier to distinguish them.
Being a downstream port we don't need to bother with gateway and DNS settings for the Ethernet port.
- Configure
dnsmasq.
At the bottom of /etc/dnsmasq.conf add:
interface=eth0
#bind-interfaces # Causes silent failure on first boot because there's no eth0 to bind to at that time. Luckily, seems unnecessary.
#listen-address=192.168.2.1 # fails with “cannot assign requested address” because it’s redundant: https://forums.raspberrypi.com/viewtopic.php?p=1704404#p1704404
dhcp-range=192.168.2.50,192.168.2.100,12h
#server=1.1.1.1 # Forward DNS requests to Cloudflare. Not necessary at this level.
domain-needed # Don't forward short names
bogus-priv # Never forward addresses in the non-routed address spaces.
This configuration was the best I could find to ensure that a good working state would be established regardless of the sequence of power on and cable connections.
- Finally, packet forwarding.
In /etc/sysctl.conf uncomment net.ipv4.ip_forward=1. This configures the kernel to be happy to redirect packets that arrive on one interface to another. Otherwise the kernel acts like a normal host and just drops packets not intended for itself.
There's an equivalent for IPv6: net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding=1, but I was able to get away with riding IPv4 a little longer. YMMV.
Now the kernel is happy, set up the forwarding:
sudo iptables -F # Flush all the chains (ie. delete all the rules) in the default "filter" table
sudo iptables -t nat -F # Do the same for the "nat" table
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o wlan0 -j MASQUERADE # perform SNAT "the liberal way" by pretending to be the source of every outgoing packet
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i wlan0 -o eth0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # then forward anything we inititiated coming back in on Cellular, out to Ethernet, as if weren't here
sudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o wlan0 -j ACCEPT # and vice versa
Make sure the forwarding sticks through reboots by saving the configuration and repeating it when the network interface comes up.
sudo iptables-save > pi-gateway.conf
sudo mv pi-gateway.conf /etc/pi-gateway.conf
Create /etc/network/if-up.d/iptables with contents:
#!/bin/sh
iptables-restore < /etc/pi-gateway.conf
Make it executable, and the Pi is baked ready for serving!
sudo chmod +x /etc/network/if-up.d/iptables
Reboot, test and monitor journalctl -u dnsmasq for any issues.
- Reference: this is an abridged version of my solution for sharing a cellular dongle over Ethernet. There's a bit more opinionated commentary in that article.