So far, my ignorance was bliss.
I was able to control the GPIO pins and for many years, the world made sense to me
But then I saw this:
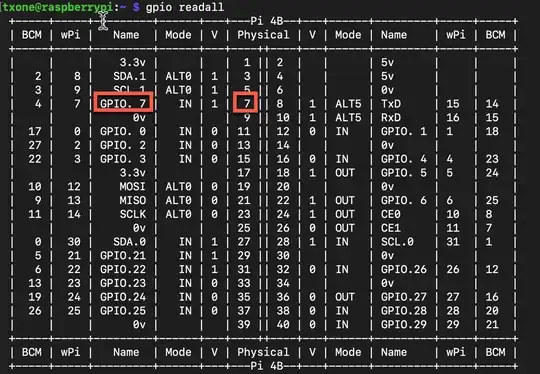
And wires got crossed in my brain
Why does it say that GPIO7 is at pin 7 of the 40pin connector, while this documentation https://www.raspberrypi-spy.co.uk/2012/06/simple-guide-to-the-rpi-gpio-header-and-pins/ says that GPIO7 is at pin 26 ? (and that is how I have been using it for years)
Are those two different "standards"? and which one is to be used when?
PS: I'm running Raspbian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye)on a rpi4
thank you for helping to get my sanity back
chrisV