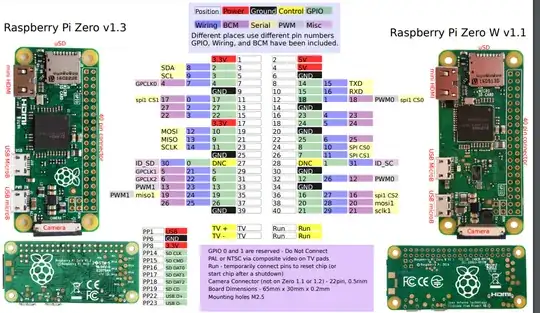
On the below diagram I understand what position (on the board), GPIO (abstract Pi GPIO numbers) and BCM (SoC pin numbers) pin numbers mean, but what's the meaning of the "wiring"?
2 Answers
"Wiring" refers to the wiring pi library, and its associated command line utility - gpio.
If you have installed Wiring Pi, you may list/print the relationship between the various RPi GPIO designations as follows:
$ gpio readall
The result on my RPi 4B is:
+-----+-----+---------+------+---+---Pi 4B--+---+------+---------+-----+-----+
| BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM |
+-----+-----+---------+------+---+----++----+---+------+---------+-----+-----+
| | | 3.3v | | | 1 || 2 | | | 5v | | |
| 2 | 8 | SDA.1 | IN | 1 | 3 || 4 | | | 5v | | |
| 3 | 9 | SCL.1 | IN | 1 | 5 || 6 | | | 0v | | |
| 4 | 7 | GPIO. 7 | IN | 1 | 7 || 8 | 1 | IN | TxD | 15 | 14 |
| | | 0v | | | 9 || 10 | 1 | IN | RxD | 16 | 15 |
| 17 | 0 | GPIO. 0 | IN | 0 | 11 || 12 | 0 | IN | GPIO. 1 | 1 | 18 |
| 27 | 2 | GPIO. 2 | IN | 0 | 13 || 14 | | | 0v | | |
| 22 | 3 | GPIO. 3 | IN | 0 | 15 || 16 | 0 | IN | GPIO. 4 | 4 | 23 |
| | | 3.3v | | | 17 || 18 | 0 | IN | GPIO. 5 | 5 | 24 |
| 10 | 12 | MOSI | IN | 0 | 19 || 20 | | | 0v | | |
| 9 | 13 | MISO | IN | 0 | 21 || 22 | 0 | IN | GPIO. 6 | 6 | 25 |
| 11 | 14 | SCLK | IN | 0 | 23 || 24 | 1 | IN | CE0 | 10 | 8 |
| | | 0v | | | 25 || 26 | 1 | IN | CE1 | 11 | 7 |
| 0 | 30 | SDA.0 | IN | 1 | 27 || 28 | 1 | IN | SCL.0 | 31 | 1 |
| 5 | 21 | GPIO.21 | IN | 1 | 29 || 30 | | | 0v | | |
| 6 | 22 | GPIO.22 | IN | 1 | 31 || 32 | 0 | IN | GPIO.26 | 26 | 12 |
| 13 | 23 | GPIO.23 | IN | 0 | 33 || 34 | | | 0v | | |
| 19 | 24 | GPIO.24 | IN | 0 | 35 || 36 | 0 | IN | GPIO.27 | 27 | 16 |
| 26 | 25 | GPIO.25 | IN | 0 | 37 || 38 | 0 | IN | GPIO.28 | 28 | 20 |
| | | 0v | | | 39 || 40 | 0 | IN | GPIO.29 | 29 | 21 |
+-----+-----+---------+------+---+----++----+---+------+---------+-----+-----+
| BCM | wPi | Name | Mode | V | Physical | V | Mode | Name | wPi | BCM |
+-----+-----+---------+------+---+---Pi 4B--+---+------+---------+-----+-----+
ICYI:
The original wiring Pi library was developed by Gordon Henderson, and maintained by him until August, 2019. Wiring Pi remains available through GitHub, but its future is not entirely clear. As the current maintainers have indicated:
... this repository has become a mirror of the last "official" source release, plus a fork facilitating updates to support newer hardware (primarily for use by the ports) and fix bugs.
- 23,558
- 5
- 42
- 83
They are numbers which may be used by the wiringPi C library and some software built on that library.
- 71,852
- 5
- 76
- 108