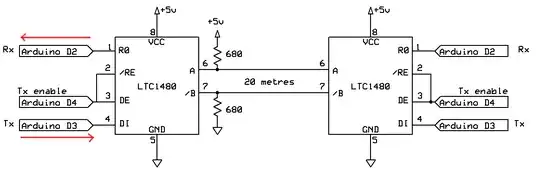
I am reading the value of six potentiometers with a TX Arduino and receiving that data and applying those numbers to a motor using serial. It is working fine through TTL but I am going to need to do this over a 60 ft tether.
I have done a little research and see that I could use RS 232 but that the maximum you should go with that is 50 ft, which will not work if I'm not mistaken. I have also seen RS 485 which will give us 4000 ft, which is overkill but will work. However, that only offers one-way communication, if I'm not mistaken. What I'm wondering is which protocol should I convert it to, and how I would have to adjust my RX and TX code.
TX code:
/*
Transmitting Code
Reads potentiometers and sends them through serial
*/
int data [10]; // to send bytes
int start [2];
int pot0Pin = A0; // analog pin used to connect the potentiometer
int pot0; // variable to read the pot0ue from the analog pin
int pot1Pin = A1;
int pot1;
int pot2Pin = A2;
int pot2;
unsigned char checksum0;
unsigned char checksum1;
unsigned char checksum2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial1.begin(9600);
pinMode(19, INPUT);
pinMode(18, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// READ THE POTENTIOMETERS:
pot0 = analogRead(pot0Pin); // reads the value of the potentiometer (pot0ue between 0 and 1023)
data[0] = pot0 & 0xFF; //least significant 8 bit byte
data[1] = (pot0 >> 8); //most significant 2 bits
pot1 = analogRead(pot1Pin);
data[2] = pot1 & 0xFF;
data[3] = (pot1 >> 8);
pot2 = analogRead(pot2Pin);
data[4] = pot2 & 0xFF;
data[5] = (pot2 >> 8);
// CREATE CHECKSUMS:
checksum0 = ~(data[0]+data[1]) + 1;
checksum1 = ~(data[2]+data[3]) + 1;
checksum2 = ~(data[2]+data[3]) + 1;
// WRITE VALUES AND CHECKSUMS TO SERIAL:
Serial1.write(data[0]);
Serial1.write(data[1]);
Serial1.write(data[2]);
Serial1.write(data[3]); //bytes sent
Serial1.write(data[4]);
Serial1.write(data[5]);
Serial1.write(checksum0);
Serial1.write(checksum1);
Serial1.write(checksum2); // send the checksum
delay(10); // delay in between reads for stability
}
RX code:
/*
Receving Code
Reads bytes from Transmitting Code and put thems back together
Applies the read bytes to our motor control board
*/
unsigned char val[10]; // variable to read the value from the analog pin
int motorVal;
int coolVal; // 0-1024 received from serial
int coolVal1;
int coolVal2;
unsigned char checksum1;
unsigned char checksum2;
unsigned char checksum3;
unsigned char checkit1;
unsigned char checkit2;
unsigned char checkit3;
int directionPin = 8;
int PWM_out_pin = 9; // works on pins 2 - 13 and 44 - 46
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial1.begin(9600);
// Serial1.begin(9600);
pinMode(10, INPUT);
pinMode(18, OUTPUT);
pinMode(8, OUTPUT);
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial1.available()>5) {
val[0]=Serial1.read(); // least significant 8 bits
val[1]=Serial1.read(); // most significant 2 bits
val[2]=Serial1.read();
val[3]=Serial1.read();
val[4]=Serial1.read();
val[5]=Serial1.read();
checksum1=Serial1.read();
checksum2=Serial1.read();
checksum3=Serial1.read();// get the checksum last
checkit1 = val[0]+val[1]+checksum1;
checkit2 = val[2]+val[3]+checksum2;
checkit3 = val[4]+val[5]+checksum3;
if (checkit1==0); {
coolVal = val[1]<<8 | val[0]; }
if (checkit2==0); {
coolVal1 = val[3]<<8 | val[2];}
if (checkit3==0); {
coolVal2 = val[5]<<8 | val[4];
}
Serial.print(coolVal);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(coolVal1);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.println(coolVal2);
delay(10);
}
// FOR MOTOR 1 (more will be added once we achieve successful serial):
if (coolVal > 550) {
digitalWrite (directionPin, HIGH);
motorVal = map(coolVal, 550, 1023, 0, 1023);
analogWrite (PWM_out_pin, motorVal / 4); }
if ((coolVal < 550) && (coolVal > 500)) {
digitalWrite (directionPin, HIGH);
analogWrite (PWM_out_pin, 0); }
if (coolVal < 500) {
digitalWrite (directionPin, LOW);
motorVal = map(coolVal, 0, 500, 1023, 0);
analogWrite (PWM_out_pin, motorVal / 4); }
}